Have you ever woken up with a sore or swollen tongue and wondered, Why do I bite my tongue in sleep? You’re not alone; many people experience this frustrating habit without even realizing it. It can be painful, confusing, and even a little scary when you don’t know what’s causing it. If this sounds like you, you’re probably searching for answers to finally understand what’s happening at night.
In this blog, we’ll break down the common reasons behind biting your tongue while sleeping and what you can do to stop it. From stress and teeth grinding to sleep disorders and jaw issues, we’ll explain it all in simple terms. You’ll also discover practical tips and solutions to protect your tongue and improve your sleep, so you can wake up feeling pain-free and at ease.
Tongue Biting While Sleeping Causes
There are several reasons you could be biting your tongue while asleep. Some are dental, some neurological, and others behavioral or physical.
Often, tongue biting is a symptom rather than the root problem; you must address the underlying cause for lasting relief.
Bruxism
Grinding or clenching your teeth, known as bruxism, is one of the top causes of tongue biting in sleep. During episodes of bruxism, your jaws press hard, and the tongue can get caught between your teeth.
Bruxism may happen while you’re asleep or even during the day. It’s often linked to stress, anxiety, or bite misalignment. If you have worn tooth surfaces, jaw pain, or frequent headaches, it may point to sleep bruxism.
Facial Muscle Spasms
Sometimes, involuntary spasms in the jaw or facial muscles can cause sudden movements that press the tongue into harm’s way. These spasms may happen from neurological conditions or as a side effect of certain drugs or nerve irritation.
When a spasm strikes in sleep, you lose voluntary control, and your tongue may be bitten. Often, people experience tremble or jaw twitching before noticing tongue injury.
Illicit Drug Use
Recreational drugs, especially stimulants like MDMA or ecstasy, can intensify bruxism or trigger involuntary chewing. These effects may lead to aggressive tongue biting.
Even after the effects wear off, your risk remains elevated if such use becomes habitual. If tongue biting correlates with drug use, cessation and medical supervision are essential.
Lyme Disease
Though not common, Lyme disease can contribute to tongue biting. The disease impacts the nervous system and may disrupt reflex pathways controlling muscle coordination.
If you also experience symptoms like fatigue, pain, rashes, or neurological signs, Lyme disease might be a complicating factor in your nighttime tongue injury.
Nighttime Seizures
Epilepsy or nocturnal seizures can cause involuntary jaw clenching that injures the tongue. Often these bites are severe, with cuts or bruises on the tongue’s edges.
If tongue biting aligns with sleep disturbances or unexplained nighttime episodes, consult a neurologist. An EEG or sleep study may reveal seizure activity you were unaware of.
Rhythmic Movement Disorder
Rhythmic movement disorder (RMD) involves repetitive body motions during sleep head banging, rocking, or jaw movements. These motions can push the tongue into dangerous positions.
While it’s often seen in children, adults may also experience mild forms of RMD, especially when under stress or recovering from illness.
Sleep Apnea
Although sleep apnea doesn’t directly cause tongue biting, its associated muscle relaxation and airway obstruction can create conditions for tongue injury. A relaxed tongue in a narrow airway may be pressed between teeth.
People with sleep apnea often also grind their teeth, compounding the risk. If you snore loudly, gasp for air, or feel daytime sleepiness, sleep apnea should be evaluated.
Read More Article: How Long Does Invisalign Take?
Biting Tongue While Sleeping Symptoms
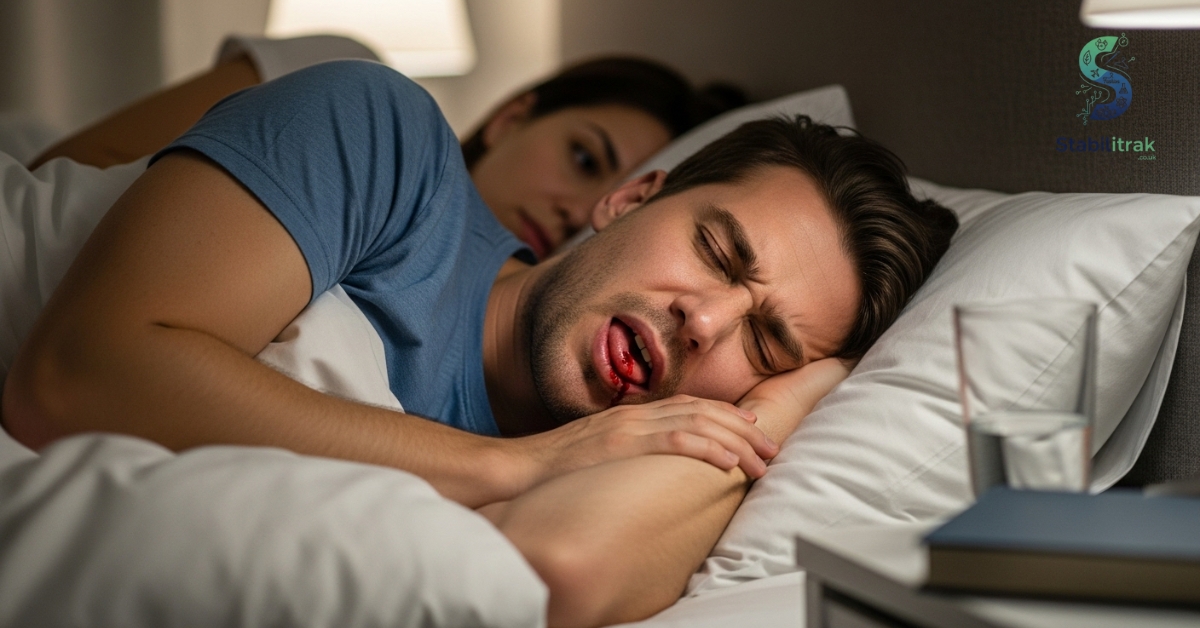

It’s not always obvious you’ve bitten your tongue. Look for signs such as:
- White, scalloped edges or raised lines on the tongue
- Cuts, ulcers, or raw areas
- Swelling or redness
- Pain, bleeding, or soreness in the morning
These symptoms indicate repeated trauma and can worsen if untreated.
Read More Article: How Long Does a Filling Take?
Tongue Biting Treatment
The key is treating the cause, not just covering up the injury.
- Nightguards / Mouthguards: A custom-fitted oral appliance helps buffer your tongue from your teeth during grinding.
- Dental correction: For malocclusion, braces or aligners may realign the bite and reduce tongue interference.
- Neurological care: If seizures or muscle spasms are responsible, neurologists may prescribe antiseizure medications or neuromodulators.
- Lifestyle modifications: Stress reduction, quitting smoking, moderating drug use, and improving sleep quality can help.
Tongue Biting in Sleep Prevention
Preventing bite injury involves a multi-pronged approach:
- Wear a custom nightguard consistently
- Undergo a sleep study to identify apnea or seizures
- Practice relaxation techniques (meditation, deep breathing)
- Avoid stimulants or drugs known to aggravate bruxism
- Maintain regular dental and medical check-ups
These steps help reduce trauma while you work on solving the core issue.
Sleep Study
A sleep study helps detect conditions like sleep apnea or seizure activity. You may use a home-based kit or stay overnight in a sleep lab. Sensors record brainwaves, heart rate, breathing, and muscle tone.
Results guide targeted treatments like a CPAP machine for apnea or anticonvulsants for seizures to reduce tongue biting.
Mouthguard
A mouthguard fitted by a dentist can absorb grinding force and prevent your tongue from being trapped between teeth. It doesn’t stop bruxism itself but protects soft tissue.
Choose a guard that covers the bite surfaces, is comfortable, and doesn’t restrict tongue movement.
Reduce Stress
Stress often worsens involuntary jaw activity.
Daily practices like meditation, deep breathing, light exercise, or counseling can lower your tension.
When stress is under control, your jaw is less likely to clench aggressively during sleep.
Don’t Use Illegal Drugs
Stimulants like MDMA, cocaine, or amphetamines often increase the risk of bruxism and tongue biting. Quitting these substances is critical.
If dependency is a problem, seek help via rehabilitation or medical support.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be needed:
- Anticonvulsants for seizures
- Muscle relaxants or botulinum toxin injections for spasms
- Anxiety medications or therapy for stress-related grinding
Always work with a medical professional for dosing and suitability.
Read More Article: The 4 Types of Grace Explained
Conclusion
Biting your tongue in sleep is painful, but not hopeless. The reason often lies in a deeper cause bruxism, apnea, seizures, malocclusion, or muscle spasms. Wear a protective nightguard, pursue medical evaluation, manage stress, and avoid risk factors like drugs or stimulants.
When you combine protection with treatment, your tongue and your mornings stand a better chance at healing.
FAQS
What does it mean when you bite your tongue in your sleep?
It often signals teeth grinding, jaw clenching, stress, or a sleep disorder like sleep apnea or seizures. Seeing a dentist or doctor can help identify the cause.
What sleep positions prevent tongue biting?
Sleeping on your side or slightly elevated can reduce pressure on your jaw and keep your tongue from slipping between your teeth.
What is tongue biting a symptom of?
It may point to bruxism, malocclusion, sleep apnea, nighttime seizures, or high stress levels.
What is the spiritual meaning of biting your tongue in your sleep?
Some believe it symbolizes holding back words, emotions, or unresolved tension in your waking life.
What does biting your tongue mean in Islam?
In Islamic teachings, biting one’s tongue can metaphorically mean refraining from saying something harmful or unkind.
What is the meaning behind biting your tongue?
It’s often a sign of self-restraint, stress, or subconscious habits—either literal or symbolic.
Are there any medical conditions linked to lip biting?
Yes. Bruxism, anxiety disorders, seizures, and some medications or drugs can cause involuntary lip or tongue biting.
What does the tongue symbolize in dreams?
The tongue can symbolize communication, honesty, self-expression, or hidden truths.
What does it mean if you bite your tongue in your dream?
It may represent holding back your words or experiencing stress you haven’t addressed consciously.
What organ does the tongue represent?
In traditional Chinese medicine, the tongue is linked to the heart and digestive system as a reflection of inner health.
What can your tongue tell you about your heart?
Changes in color, swelling, or coating can sometimes signal heart or circulatory issues in holistic traditions.
What are the warning signs on the tongue?
Persistent sores, discoloration, swelling, or scalloped edges can be warning signs of stress, infection, or systemic illness.
Can heart disease affect your tongue?
Yes, poor circulation or certain heart conditions may lead to a pale, swollen, or bluish tongue.
Can stress affect your tongue?
Definitely. Stress can cause clenching, bruxism, ulcers, and even tongue soreness or scalloping.
Can you tell someone’s health by their tongue?
Often, yes. The tongue’s color, texture, and coating can reveal hydration, nutrition, or systemic health issues.
What are the signs of dehydration on your tongue?
A dry, cracked, or sticky tongue with a rough surface may indicate dehydration.
What does your tongue tell you about your liver?
In holistic practices, a swollen or coated tongue may signal liver imbalance, though medical testing is needed for confirmation.







1 thought on “Why Do I Bite My Tongue in Sleep? Explained Simply”