English grammar can be perplexing at times, in particular when getting to know verb paperwork. One of the most essential topics in grammar is regular and irregular verbs. Those verbs help us speak about moves inside the past and play a chief function in talking and writing English efficiently. This article explains regular and irregular verbs in a clean and easy way, with smooth rules and useful examples.
Introduction to Regular And Irregular Verbs
Verbs display actions, events or states of being. At the same time as we communicate approximately something that already passed off, we use the past tense. In English, verbs are divided into two main types based totally on how they form the past tense: regular verbs and irregular verbs. Understanding how they work makes conversation clearer and greater confidence.
Rules of Regular and Irregular Verbs
Regular verbs follow a predictable rule to form the past tense, at the same time as irregular verbs change in different ways. Due to this distinction, learners should exercise each type carefully to keep away from errors.
Regular Verbs Defined
Regular verbs form their past tense and past participle through adding -ed, -d, or -ied to the base form.
As an example:
- talk → talked
- close → closed
- study → studied
These verbs are easy to apply because they comply with the equal pattern. Once beginners recognize the rule, they can apply it to many verbs without confusion. Regular verbs additionally help improve sentence flow and readability in each writing and talking.
Irregular Verbs Defined
Irregular verbs do not follow a set rule when changing into the past tense. Every verb has its own form, which must be discovered one at a time.
As an example:
- go → went
- eat → ate
- write → wrote
Even though irregular verbs may additionally seem hard at the start, they may be very not unusual in ordinary English. Gaining knowledge of them through studying, listening and exercise helps learners use them clearly.
Read More Articles: How To Improve Yourself
Key Differences Between Regular and Irregular Verbs
| Regular Verbs | Irregular Verbs |
| Follow clear rules | No fixed rules |
| Add “-ed” or similar endings | Change form completely |
| Easy to predict | Need memorization |
| Example: clean → cleaned | Example: see → saw |
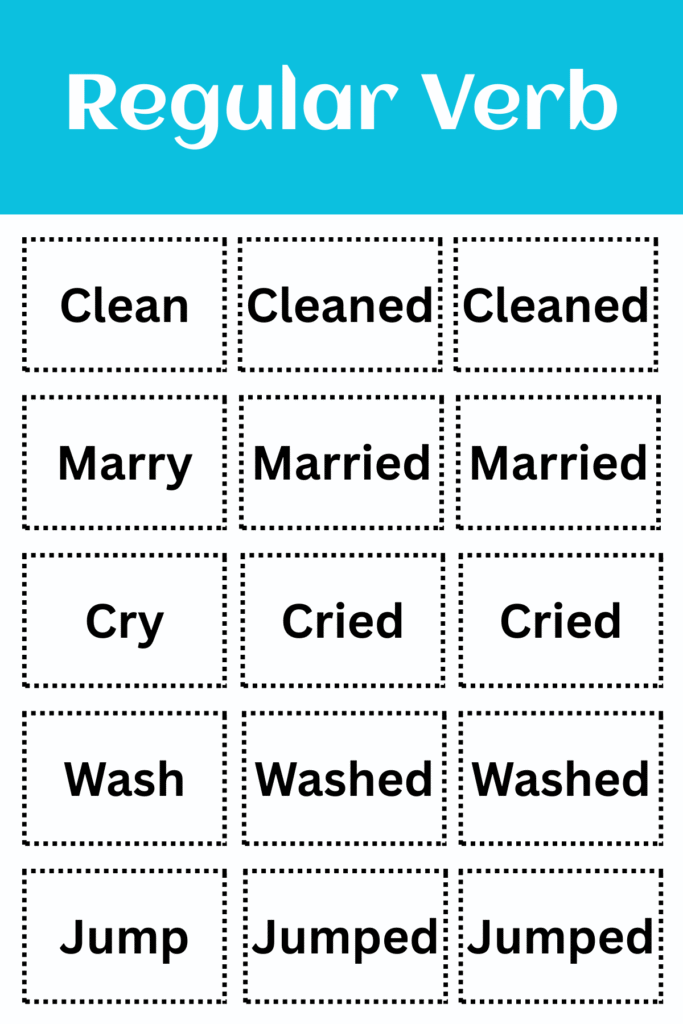
Examples of Regular Verbs
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
| Walk | Walked | Walked |
| Play | Played | Played |
| Finish | Finised | Finised |
| Help | Helped | Helped |
| Listen | Listened | Listened |
| Agree | Agreed | Agreed |
| Hurry | Hurried | Hurried |
| Plan | Planed | Planed |
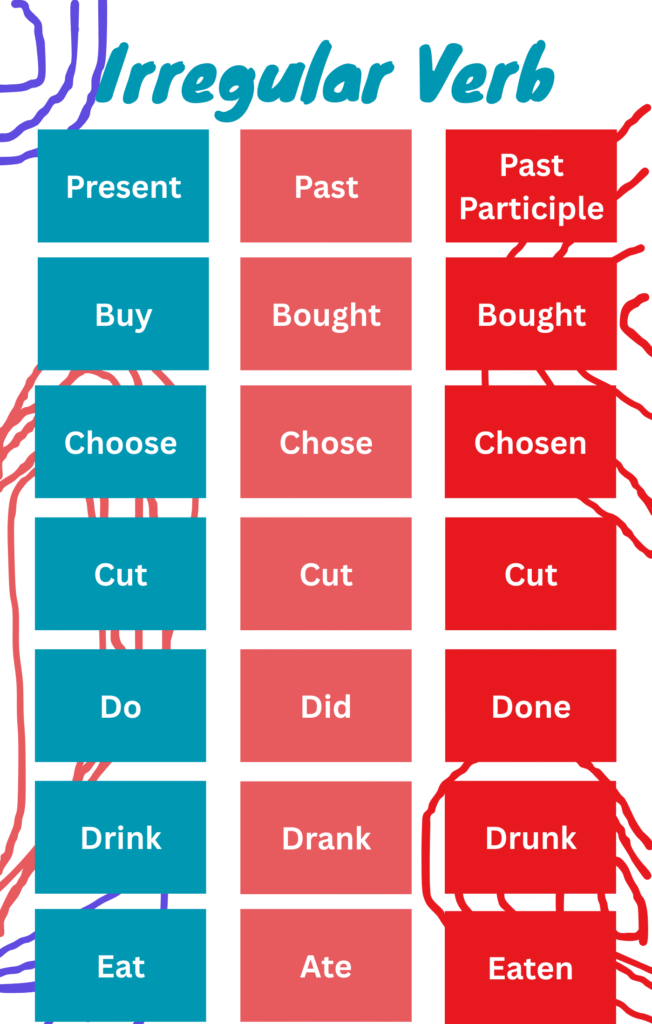
Examples of Irregular Verbs
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
| go | went | gone |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| see | saw | seen |
| write | wrote | written |
| make | made | made |
| take | took | taken |
| come | came | come |
| give | gave | given |
Common Mistakes Learners Make
Many learners struggle with verb forms, in particular inside the past demanding. A common mistake with regular verbs is inaccurate spelling, such as writing “stoped” in preference to “stopped.”
With irregular verbs, learners often follow regular guidelines incorrectly, for example saying “buyed” in preference to “bought.” Another frequent error is using the incorrect past participle, such as “I have saw” in place of “I have seen.”
Regular practice and revision can help avoid these mistakes.
Read More Articles: The Beauty Of Nature
Conclusion
Regular and irregular verbs are a key part of English grammar. Regular verbs are simple and rule-based, while irregular verbs require greater interest and practice. By learning both types and using them in sentences, learners can improve their grammar skills and speak extra confidently in English.

AI-powered SEO content writer with 3 years of experience in creating clear, helpful, and search-engine-optimized content using AI and human research.






